Introduction
UFP Hair Restoration specialists understand that hair loss doesn’t affect just men and see many women for hair restoration in Utah as well. There are many effective solutions for women facing hair loss that our hair restoration specialists offer through individualized treatment plans.
What Is Female Pattern Hair Loss?
While more common in men, females often experience the devastating effects of hair loss as well. Both female pattern hair loss and male pattern baldness are medically referred to as androgenic alopecia. While considered the same condition, the pattern in which hair loss is experienced is very different between the two genders.
Men with androgenic alopecia tend to lose hair starting at the temples, vertex, and/or crown of the head. With women, the hair loss pattern spreads across the top of the scalp. The back of the head is least affected. There are varying levels of severity according to the Ludwig Classification. Even in advanced stages of hair loss, the affected area typically does not become completely bald and the hairline remains intact.
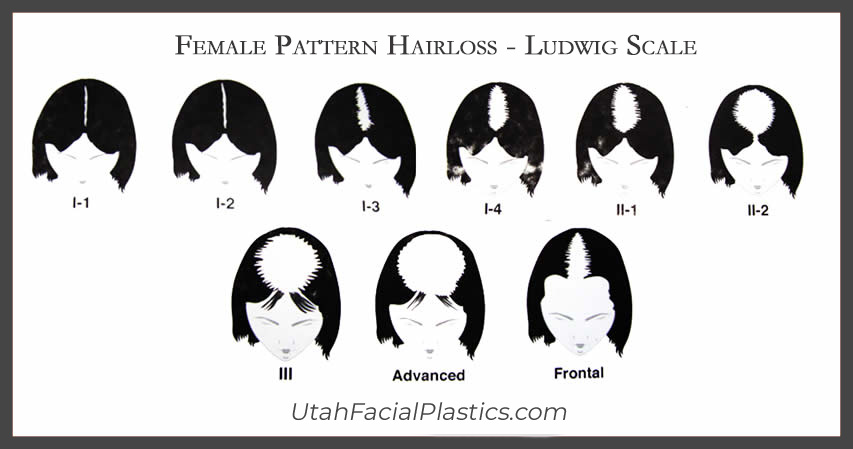
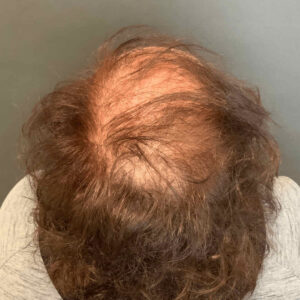
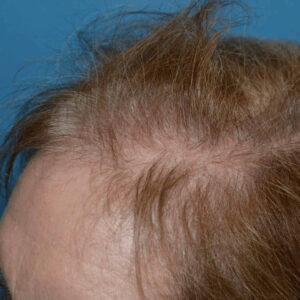
Most women with female pattern hair loss notice an increase in hair shedding before they become aware of hair loss over the crown. Others may not notice their hair shedding but feel they’ve lost hair volume and body. The shedding and thinning process typically come in a series of episodes that occur progressively closer together, until some women find they are shedding all year round.
The average person sheds 50-100 hairs a day, which usually doesn’t cause thinning because new hair is growing in at the same time. With female pattern baldness, the follicles produce shorter, thinner miniaturized hair strands that continue to thin and decrease in size with the process of miniaturization. In men, follicles eventually go dormant while they remain miniaturized in women.
Other Causes Of Hair Loss In Women
Though Androgenic Alopecia (Female Pattern Hair Loss) is the most common reason for permanent hair loss for women, there are many others. And women are typically more affected by non-AGA causes of balding than men, with the main cause being genetics or male pattern baldness.
Other common reasons for female hair loss include:
- Thyroid Conditions
- Pregnancy
- Medication
- Stress
- Menopause
- Extreme Weight Loss
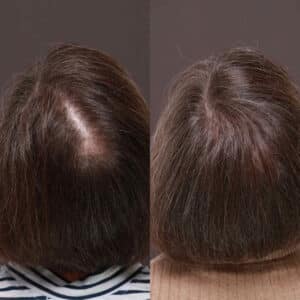
It’s important to discuss your medical history with your hair specialist at a complimentary consultation at UFP Hair Restoration in Utah or online. UFP experts will complete a thorough health assessment and discuss non-surgical options for hair loss and/or possibly hair transplant surgery to help you achieve your goals. Drs. Thompson, Henstrom, and Manning offer the most advanced options available for hair restoration today and will provide you with the best results possible.
Contact Us Today!
Interested in getting treatment for female hair loss in Salt Lake City, Draper, Layton, Utah and the surrounding areas? Contact UFP Hair Restoration for more information or to schedule a hair restoration consultion call 801.849.8140.