Fact: Two-thirds of American men age 35 and younger experience male pattern baldness. Hair loss is an extremely personal and emotional loss for many men (and women) some of whom start losing it before they even hit their twenties. Unfortunately, we don’t get to opt in or out of the male or female pattern baldness gene, but thankfully, these days, we do get to choose how we handle it. Today there are more hair restoration options than ever before available to those wanting to replace those lost hair follicles.
Hair Loss Causes That Hair Restoration Could Address
Many patients looking for hair restoration in Utah come to see Drs. Thompson, Henstrom, and Manning of UFP Hair Restoration to discuss hair replacement surgery. Hair loss typically results from a combination of normal aging, changes in hormones, and/or a family history of baldness. Baldness is not caused by poor circulation to the scalp, vitamin deficiencies, dandruff, or excessive hat wearing, despite some of the myths you may read or hear. Other myths that are not true are that hair loss can be determined by looking at your maternal grandfather or that if you have a full head of hair by age 40, you’ll never lose it. It is true that the earlier the hair loss begins, the more severe the baldness will become.
Hair Transplant Specialists In Salt Lake City
As fellowship trained hair restoration specialists in Utah, UFP Hair Restoration Drs. Thompson, Henstrom, and Manning are known for incredibly natural results. Patients appreciate that others notice improvement but cannot tell they’ve had a hair restoration procedure because the hair grafts have been placed to the thinning area in a way that is completely natural. Following hair transplant surgery, patients report greater confidence and self-assurance and are astounded at how simple and painless the process is.
Patients also appreciate our hair restoration specialists' genuine concern for their well-being and satisfaction. They are committed to ethical, caring, and honest treatment of their patients and work very hard to earn and maintain their trust. Although patient care is their primary focus, their academic, research, and teaching abilities have been recognized throughout their careers with numerous awards as well as several scholarly publications. In addition, UFP was voted "Best Cosmetic Surgery Center" and "Best Medical Spa" for Best of Utah, Best of SLC, and Best of Northern Utah in 2023.

How Hair Loss Starts, How To Manage, & When To Intervene
Testimonial

"I am very happy with my results. Dr. Thompson really cares about his patients and I like that about him. I think it’s great to have more confidence and am a true believer in success as attitude. If you have the right attitude, then you’re going to be successful. It’s going to draw people to you and it’s not a vanity thing. Life’s about choices…you have to change things yourself."
Hair Restoration Results
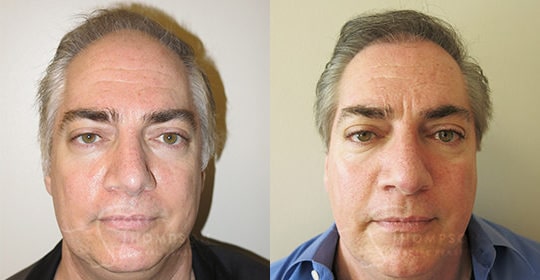
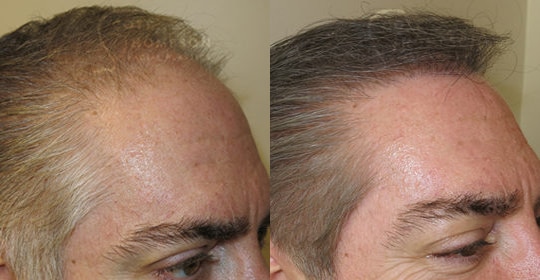
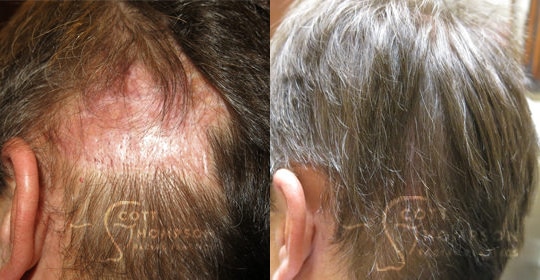
Hair Restoration Results From Utah’s Top Facial Plastic Surgeon and Specialist
Frequently Asked Questions
Hair transplantation at UFP Hair Restoration involves removing small pieces of hair-bearing grafts from another area of the head (donor site) and relocating them to the bald or thinning area for a completely natural result. This can be done through a variety of techniques, most commonly Follicular Unit Grafting (strip from the back of the head) and Follicular Unit Extraction (individual grafts) with Neograft. They are both very successful and specific to each individual patient’s needs and concerns.
Patients who decide to undergo hair replacement surgery come in for a consultation with one of our specialists to determine the best course of treatment and how many grafts are needed for the desired result. Sometimes prescriptions are given to maximize the results of hair replacement surgery.
Drs. Scott Thompson, Douglas Henstrom, & James Manning have extensive experience performing hair transplant surgery. During your consultation, they will discuss your concerns as well as your goals and motivations for surgery. An exam and review of your current and previous health history will also take place.
They will then examine the thinning area of concern and determine how large of an area will need to be harvested to help you achieve your goals. Discussion about different hair replacement surgery options will take place and together you will determine the possible plan for you and your specific needs.
The two main techniques our surgeons utilizes to perform hair transplant surgery are Follicular Unit Transplant (strip method or FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT is performed by taking a strip of hair from the back of the head and extracting each follicle that is then transplanted to the thinning areas of the scalp. This method is very common and when the incision is closed properly by an experienced facial plastic surgeon, the incision will fade to a faint line that can be hidden underneath the hair.
Follicular Unit Extraction is a sub-type of FUT. As with both techniques, Drs. Thompson and Henstrom artistically place the extracted follicular units into the thinning or bald area in the same natural looking fashion. The difference lies in the way the follicular units are extracted from the scalp. While a strip of hair is taken during an FUT procedure, each follicular unit is harvested one at a time during FUE. When performed manually, FUE can be time-consuming, tedious, with a lower graft survival rate.
The Neograft device eliminates the problems associated with manual FUE hair restoration. Follicular units are suctioned during an automated process for a much simpler, quicker and more effective process than either FUE or FUT for hair restoration.
Follicular Unit Transplant surgery (FUT or strip method) is a time-tested technique for permanent hair restoration in SLC, Utah. Drs. Thompson, Henstrom and Manning, double board-certified facial plastic surgeons, use your own hair to restore thick, healthy hair to balding areas and can recreate your natural hairlines with the most natural results.
FUT involves taking the transplantation of tiny follicular units of hair that are extracted from areas of strong hair growth that are more resistant to balding – typically the back and sides of the scalp – which are then implanted to thinning or bald areas of the head. Drs. Thompson and Henstrom’s extensive experience with hair restoration techniques, medical expertise, and attention to detail produce incredibly natural results for patients concerned with hair loss.
In comparison to older, traditional methods, our surgeons are able to achieve successful outcomes by dissecting the harvested hair into very small sections, called follicular units, and placing them in tiny grafts that are virtually undetectable. These results are in complete contrast to those of hair “plugs” from hair transplant surgery years ago.
Follicular Unit Extraction for successful hair restoration in Utah is a method of extracting, or harvesting, individual follicular units directly from the donor area, without the need for a linear incision.
FUE is not a completely different procedure from the strip method, follicular unit transplantation, but a sub-type of FUT. In either situation, follicular units are microscopically dissected and transplanted to areas of baldness or thinning. The real difference between FUE and FUT is the way the follicular grafts are obtained. FUT follicular units are obtained prior to dissection from a dense strip of hair while FUE follicular units are extracted one by one. The process in the recipient area is the same with either procedure.
Manual FUE methods involve plucking follicular units one at a time, increasing the chances of damage to the graft. It is also very time consuming, thus making the process very expensive. The Neograft device suctions each unit with an automated device making the process very quick and efficient. With a survival rate of 98%, it’s no surprise that Neograft has a 100% satisfaction rate on RealSelf.
Because no incisions are made, this method for hair restoration has recently gained more momentum with patients and in the media. FUE with Neograft is also particularly helpful for patients who lead active lifestyles and/or typically wear their hair very short where even a well-closed incision (as with FUT) would be noticeable.
It is completely normal for the hair contained within the follicles to fall out before establishing regrowth. Our surgeons see all of their patients repeatedly for the first month to evaluate the process and for up to a year as regrowth comes in. Some patients decide after some time that they would like additional grafts for a fuller result while most are beyond satisfied with their initial procedure.
Because every patient has a different set of goals and needs varying amounts of grafts for fullness, UFP Hair Restoration does not provide set costs for surgery. A full detailed quote is given during a complimentary consultation at our Layton and Draper locations or through a Virtual Consultation online.
The eyebrows are an important part of facial symmetry and greatly contribute to the aesthetic appearance of men and women. Eyebrows frame the eyes, typically the first facial feature others notice. It’s no wonder over-plucking or waxing can leave many feeling self-conscious about their facial appearance, despite their best efforts to draw or tattoo eyebrows on. The results of such techniques are typically unnatural and/0r short-lasting.
UFP hair restorartion specialists perform eyebrow restoration procedures in Utah often providing permanent, natural results. This can be done with the FUE or FUT method.
UFP Hair Specialist offer complimentary virtual consultations for patients that live long-distance or who are short on time. Simply contact our office to schedule a consultation via Skype or FaceTime. We will then provide you with a detailed quote immediately following your consultation. A Patient Care Coordinator will provide you with additional procedure details, dates, and information on local accommodations at that time as well.
Hair Restoration Consultation In Salt Lake City & Layton, UT
If you're considering hair loss treatment in the Utah area, call our office at 801.849.8140 or schedule a consultation with on our Utah's leading hair restoration specialists.